Enhancing Process Safety Management Through Workforce Training and Engagement
Introduction
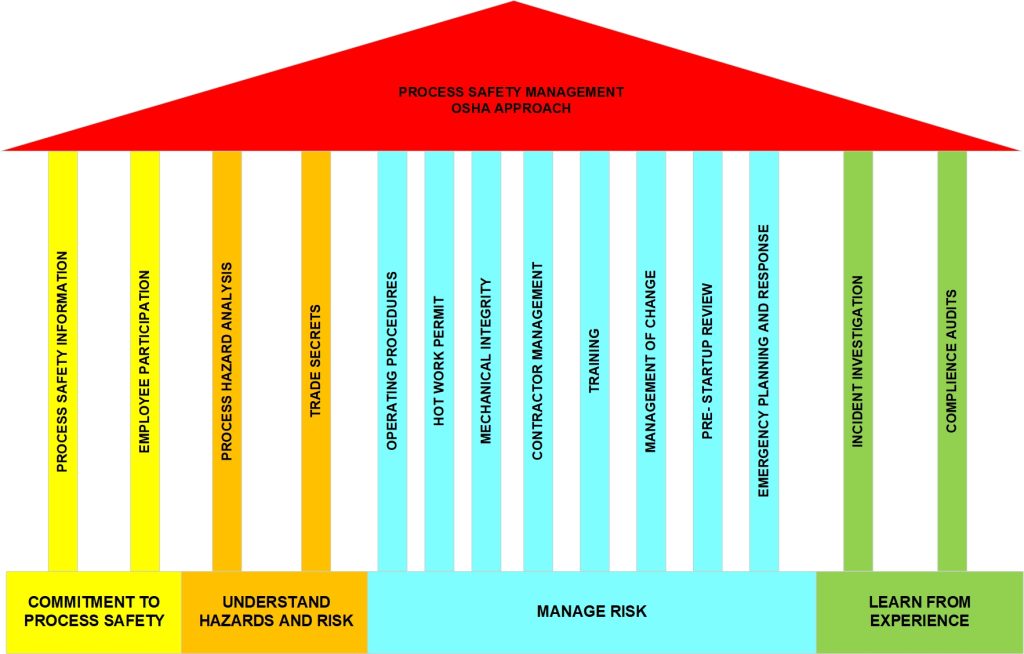
Process Safety Management (PSM) plays a crucial role in maintaining safe industrial operations. It involves a systematic approach to identifying, evaluating, and controlling hazards associated with industrial processes. One of the most effective ways to strengthen PSM is through workforce training and engagement. A well-trained workforce ensures compliance with safety protocols, reduces risks, and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Why Workforce Training is Essential for Process Safety Management
A robust training program is fundamental to improving safety standards in any industry. Proper training ensures that employees understand the risks associated with their work environment and are equipped with the necessary skills to handle emergencies.
Key Benefits of Workforce Training in PSM
- Enhanced Risk Awareness – Employees can recognize potential hazards before they escalate into critical issues.
- Regulatory Compliance – Proper training aligns with industry safety standards and legal requirements.
- Emergency Preparedness – Workers learn how to respond effectively to hazardous situations.
- Reduction in Accidents – A knowledgeable workforce minimizes human errors leading to safety incidents.
- Improved Process Efficiency – Trained employees contribute to smooth operations and better decision-making.
Developing an Effective Workforce Training Program
A structured training program is necessary to ensure that employees understand the intricacies of Process Safety Management and can implement it effectively. The following steps can help in designing an effective training program:
1. Identifying Training Needs
- Conduct risk assessments to determine key safety areas requiring training.
- Evaluate past incidents and near-misses to understand common safety lapses.
- Identify skill gaps in employees to tailor training programs accordingly.
2. Creating Customized Training Modules
- Develop training content that is specific to industry risks and safety challenges.
- Include real-life case studies and simulations for better understanding.
- Ensure training material aligns with regulatory guidelines and safety standards.
3. Implementing a Blended Learning Approach
- Use a combination of classroom sessions, on-the-job training, and digital learning.
- Conduct interactive workshops and drills to reinforce learning.
- Provide hands-on experience with safety equipment and response protocols.
4. Regular Training and Continuous Improvement
- Conduct periodic refresher courses to keep employees updated on safety protocols.
- Evaluate training effectiveness through assessments and feedback.
- Adapt training strategies based on industry advancements and regulatory changes.
Engaging the Workforce for Better Safety Implementation
Training alone is not sufficient; engaging employees in safety culture enhances the effectiveness of Safety Audits and overall risk management. Here’s how organizations can improve workforce engagement:
1. Encouraging Open Communication
- Establish a platform for employees to report hazards and share safety concerns.
- Promote a culture where feedback is welcomed and acted upon.
2. Recognizing and Rewarding Safe Practices
- Implement incentive programs for employees who demonstrate excellent safety compliance.
- Celebrate milestones and achievements in workplace safety.
3. Involving Employees in Safety Committees
- Encourage employees to participate in safety planning and decision-making.
- Assign responsibilities to workers in safety audits and inspections.
4. Conducting Safety Drills and Mock Exercises
- Regularly simulate emergency scenarios to prepare employees for real-life situations.
- Assess response times and improve protocols based on performance.
The Role of Leadership in Safety Training and Engagement
Strong leadership is essential in fostering a culture of safety. Management must take an active role in workforce training and engagement by:
- Setting Clear Safety Expectations – Leaders should define safety goals and ensure employees understand them.
- Leading by Example – Management must adhere to safety practices to encourage employees to do the same.
- Providing Adequate Resources – Investing in advanced training programs, modern safety equipment, and regular Fire Audits ensures a safer workplace.
- Encouraging Employee Involvement – Employees should feel valued in safety-related discussions and decision-making processes.
Case Studies: How Training and Engagement Have Improved Process Safety
Case Study 1: Chemical Manufacturing Plant
A large chemical manufacturing company implemented an extensive Hazop Study training program. By engaging employees in hazard identification and process optimization, they reduced safety incidents by 40% within a year.
Case Study 2: Oil Refinery Safety Enhancement
An oil refinery introduced a workforce engagement strategy that involved employees in risk assessment committees. As a result, workplace injuries decreased by 30%, and near-miss reporting improved significantly.
Case Study 3: Power Plant Training Initiative
A power generation company incorporated virtual reality (VR) training for hazardous scenarios. This interactive approach led to better safety compliance and improved response times during emergency drills.
Challenges in Workforce Training and Engagement
Despite the benefits, organizations may face challenges in implementing effective workforce training and engagement programs. Common challenges include:
- Resistance to Change – Some employees may be reluctant to adopt new safety procedures.
- Time Constraints – Training sessions may disrupt production schedules.
- Limited Resources – Smaller organizations may struggle to invest in advanced training solutions.
- Lack of Continuous Training – One-time training programs are not enough to sustain safety improvements.
Overcoming Challenges for Effective Implementation
To address these challenges, organizations should:
- Develop flexible training schedules to minimize operational disruptions.
- Utilize cost-effective training methods, such as online courses and e-learning platforms.
- Reinforce learning through regular refresher sessions and hands-on practice.
- Encourage leadership to drive safety initiatives and address employee concerns proactively.
Conclusion
Process Safety Management is an integral part of industrial safety, and its success depends significantly on workforce training and engagement. By equipping employees with the necessary skills and knowledge, organizations can reduce risks, improve regulatory compliance, and foster a culture of safety. Additionally, integrating employee engagement strategies into safety programs ensures a proactive approach to hazard identification and mitigation. Leadership commitment, continuous training, and open communication are key factors in achieving a sustainable safety culture.
For industries looking to enhance their safety performance, investing in workforce training and engagement is not just an option—it is a necessity for long-term operational success and risk mitigation.