Understanding Process Safety Management: Key Elements & Benefits
Introduction: What is Process Safety Management?
Process Safety Management (PSM) is a structured framework designed to prevent accidents and hazards in industries dealing with hazardous chemicals, high-risk operations, and complex industrial processes. It ensures that businesses follow stringent safety protocols, reducing the risk of fire, explosions, chemical spills, and other catastrophic failures.
PSM plays a critical role in industries such as oil & gas, chemical manufacturing, power plants, and pharmaceutical production, where even minor lapses can lead to severe human, environmental, and financial consequences. By implementing a robust process safety strategy, organizations can enhance workplace safety while ensuring regulatory compliance.
This article explores the key elements of Process Safety Management and the benefits it offers to industries.
What Are the Key Elements of Process Safety Management?
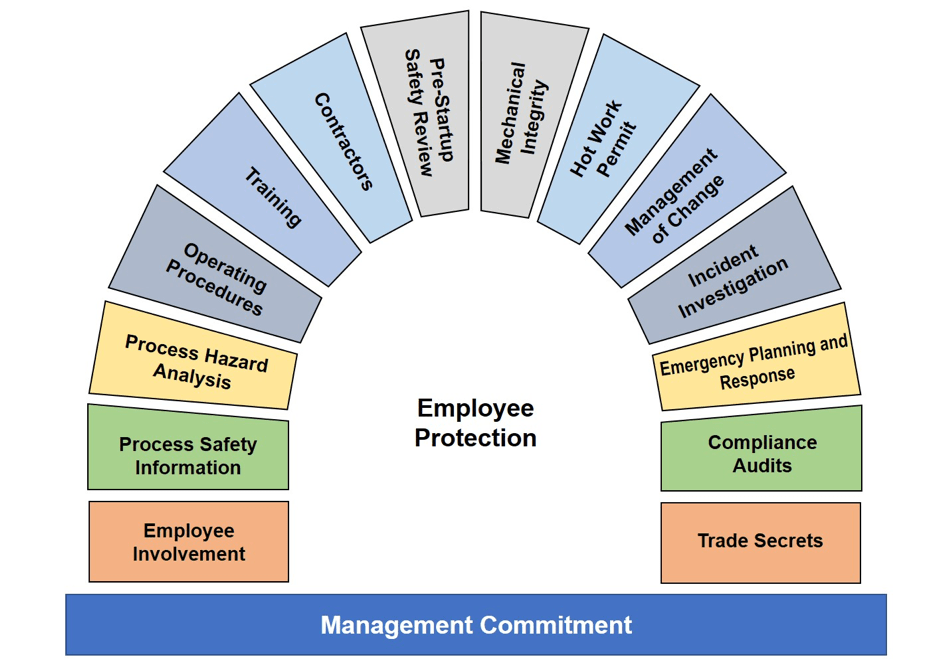
A well-structured Process Safety Management system consists of several interconnected components. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has identified 14 key elements that industries should integrate to ensure process safety and operational efficiency.
1. Process Safety Information (PSI)
Companies must maintain a detailed inventory of hazardous substances, chemical properties, and safety data sheets. This ensures that employees and safety personnel understand potential risks associated with industrial operations.
2. Process Hazard Analysis (PHA)
A Process Hazard Analysis identifies potential hazards, failure points, and risk scenarios within industrial processes. Techniques like Hazop Study help in assessing system vulnerabilities and improving preventive measures. Learn more about the Hazop Study and its role in risk assessment.
3. Operating Procedures
A well-documented Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) ensures that employees follow consistent and safe operational practices, reducing human errors and process-related accidents.
4. Employee Training & Competency Development
Comprehensive safety training programs must be conducted regularly to ensure that workers are well-equipped to handle emergencies, process failures, and hazardous chemicals.
5. Mechanical Integrity & Equipment Maintenance
Routine inspection, testing, and maintenance of critical equipment—such as pressure vessels, pipelines, and safety interlocks—help prevent catastrophic failures.
6. Management of Change (MoC)
Any modification in equipment, materials, or operational procedures must undergo a formal risk assessment before implementation. This ensures that changes do not introduce new safety hazards.
7. Pre-Startup Safety Review (PSSR)
Before initiating a new process or modifying an existing one, a safety audit should be conducted to verify that all safety measures are in place. Learn more about the importance of Safety Audit in industrial operations.
8. Emergency Preparedness & Response Planning
Having a robust emergency response plan ensures that businesses can handle incidents such as chemical leaks, fires, and equipment failures with minimum casualties and property damage.
9. Incident Investigation & Root Cause Analysis
Every safety incident should be documented, analyzed, and reviewed to identify the root cause and prevent recurrence. This ensures continuous improvement in safety procedures.
10. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Industries must adhere to local and international safety regulations, including OSHA PSM 1910.119, ISO 45001, and EPA RMP guidelines to ensure legal compliance.
By following these key elements, businesses can establish a safer workplace while minimizing operational risks.
What Are the Benefits of Implementing Process Safety Management?
The adoption of Process Safety Management provides multiple benefits, ranging from employee safety to regulatory compliance and financial stability.
1. Reduces Workplace Accidents and Injuries
By implementing structured safety protocols, businesses can prevent chemical exposure, fire hazards, and equipment malfunctions that endanger workers.
2. Ensures Regulatory Compliance
Failure to comply with safety regulations can lead to legal penalties, lawsuits, and operational shutdowns. A well-implemented PSM system ensures compliance with OSHA, NFPA, and ISO safety standards.
3. Minimizes Financial Losses and Downtime
Industrial accidents result in damaged equipment, legal liabilities, and production delays. Effective risk management strategies help companies save millions in accident-related costs.
4. Enhances Safety Culture Within the Organization
A strong safety culture promotes employee accountability, hazard awareness, and proactive risk identification. This leads to a more engaged and responsible workforce.
5. Prevents Environmental Hazards
PSM ensures the safe handling and disposal of hazardous chemicals, reducing the risk of air, water, and soil contamination.
6. Improves Business Reputation and Stakeholder Confidence
Organizations that prioritize process safety earn trust from employees, investors, and regulatory bodies. This helps in long-term business sustainability.
By integrating Process Safety Management, industries can achieve operational excellence while maintaining a safe and compliant work environment.
The Role of Safety Audits and Fire Audits in Process Safety Management
Regular audits and inspections play a vital role in Process Safety Management, ensuring that safety systems remain effective.
Safety Audits: Ensuring Continuous Improvement
A Safety Audit helps organizations identify risks, assess compliance, and improve safety performance. It provides a systematic approach to evaluating existing safety protocols. Learn more about the benefits of conducting a Safety Audit.
Fire Audits: Preventing Fire Hazards in Industries
Fires in industrial facilities can lead to loss of life, financial damage, and operational disruption. A Fire Audit assesses fire prevention strategies, emergency response plans, and firefighting equipment efficiency. Explore more about Fire Audit and its significance in fire safety planning.
These audits provide valuable insights for industries to enhance their safety framework and prevent accidents before they occur.
How Can Safety Consultants Help in Implementing Process Safety Management?
Implementing Process Safety Management requires expertise in risk assessment, regulatory compliance, and industrial safety best practices. A professional Safety Consultant helps industries identify potential hazards, conduct safety training, and implement robust risk management strategies.
Key Services Offered by a Safety Consultant
-
Risk assessment and hazard identification
-
Development of safety management frameworks
-
Employee safety training and compliance guidance
-
Implementation of fire and explosion protection measures
-
Auditing and continuous safety improvement planning
For expert guidance in safety implementation, consult a Safety Consultant who specializes in industrial safety and risk mitigation.
Conclusion: The Need for Robust Process Safety Management
Process Safety Management is not just a regulatory requirement—it is a fundamental necessity for industries dealing with hazardous materials and high-risk processes. Implementing a structured PSM framework ensures workplace safety, legal compliance, financial security, and environmental protection.
By incorporating proactive safety measures, conducting regular audits, and seeking expert guidance, businesses can create a safe, efficient, and compliant industrial environment.